These days, everyone who uses the Internet or who has a website of their own, has to be concerned about security. The prevalence and the skill of online hackers is highlighted almost daily as news stories are announced about another corporation which has suffered a security breach, with dire consequences resulting. No one really expects to be victimized by cyber attackers, but that’s exactly why they’re so effective – in many cases, grossly inadequate security measures were taken by a company, and it didn’t really take much ingenuity on the part of a hacker to penetrate their defenses.
One of the most basic steps you can take to protect your website is to ensure that all communications with other users and other websites are conducted in the safest possible manner, which means encrypting those communications. Any exchanges which are not encrypted are transmitted as simple text, which can easily be hijacked and read by criminal-minded individuals, and used for malicious purposes. That’s where SSL certificates come into the picture, and can be used to accomplish the necessary encryption.
What exactly is SSL and how does it work?
The Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) amounts to a standard security technology which was developed for the purpose of establishing an encrypted connection between a browser and a web server. This specific kind of link guarantees that any data which is passed between the two entities remains private, and cannot be read by anyone intercepting the message. The technology is already used by millions of websites to guarantee the safety of transactions between websites and any of their clients.
Creating an SSL connection requires the installation of an SSL certificate, and when you activate SSL on a given server, you will be required to answer several questions regarding the true identity of your company’s website. The web server then will create a private key and a public key, with the public key being placed into a data file which contains your company information, and which is known as a Certificate Signing Request (CSR). This CSR, must then be submitted to a Certification Authority, which will validate your company’s details, and issue an SSL certificate which allows you to make use of the technology.
Your web server will then sync up the SSL certificate which was issued to you with your private key, and you will then have an encrypted link between your website and the web browsers used by your customers. All of the real technology behind SSL remains hidden from users, and instead they will simply see a symbol next to the URL which alerts them to the fact that they are protected by SSL encryption.
All SSL certificates must be issued only to legitimate companies, or individuals which are legally accountable. The information contained in an SSL certificate will include company name, domain name, address, city, state, and country, as well as the certificate’s expiration date. There is also information included about the Certification Authority which issued the certificate.
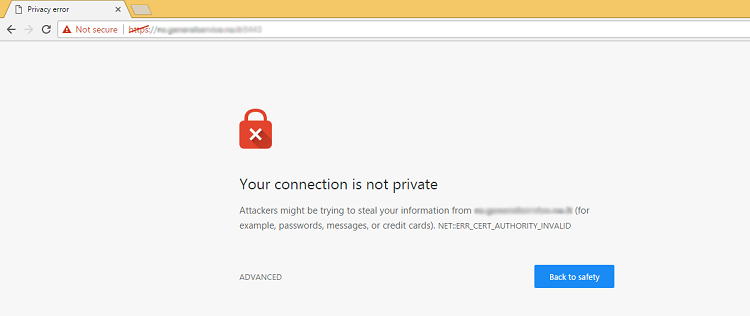
When any browser connects to a secure website, it will first retrieve the SSL Certificate and ensure that its expiration date has not yet been reached, and that the certificate has been issued by a valid Certification Authority. It must also be a certificate which was issued specifically to the company website which you are now connecting to, and if it fails on any of these validation checks, a warning message (see screenshot above) will be sent to the user informing them that the site is not secured by SSL.
Importance of SSL to Google
In 2017, Google’s chrome browser began displaying a ‘not secure’ message to users whenever they were accessing a website which did not use SSL. Google has made it mandatory for all websites to use SSL, so that user safety can be assured when browsing, and those sites which are not using SSL are clearly identified to users.
There are several reasons why SSL is so important to Google:
- One of the primary reasons is that it protects data exchanged by both user and the website they’re accessing.
- It also improves customer trust, which is a huge benefit to the website, since all customers can have confidence that their transactions are secure.
- A website protected by SSL can have its entire network secured against unscrupulous individuals who attempt to hijack exchanges or to inject malicious code into those exchanges.
- Any website with an SSL certificate has been certified to be a legitimate site, because the Certificate Authority will have confirmed your authenticity during its background investigation.
As a show of how important the SSL certificate is to Google, its search engine introduced a new algorithm in 2014 which awarded higher rankings to those sites which were using SSL technology. Several studies which have been conducted into the link between SSL technology and higher Google rankings have confirmed that this relationship exists and that Google does indeed take the issue seriously.
If you want to improve your search ranking, improving the website security by installing SSL certificate is one of the easy ways you can do.
Installing an SSL Certificate
There are three main ways that you can install an SSL certificate website, the first of which is to have your website host do it for you. Some website hosts will offer paid services and install your SSL certificate for a fee. However, if you have the time and little bit of computer savvy, you can install the SSL certificate yourself by following the instructions included here:
- In order to install the SSL certificate yourself, you must have full access and control of your web server, and you need to have following information: IP address, the SSH key authentication, the server username, the software used by your server, and the operating system and version number used by your server.
- Once you’ve gathered all this information together, you’ll need to connect to your server, and install a tool which generates the SSL certificate.
- After logging on to your server, you can send SSH commands using Terminal if you have a Mac system, or by downloading PuTTY if you’re a Windows user.
- Once you have created a Certificate Signing Request (CSR), and you’ve purchased an SSL certificate, a validation team will authenticate your request and process it.
- When the request has been validated, an SSL certificate will be issued and sent to you in an email, or you can have the certificate downloaded directly to your server.
- When installing an SSL certificate, you will also have to install what’s known as an intermediate certificate. This establishes the trust between your SSL certificate and the Certificate Authority’s certificate.
- In order for the certificate trust chain to be completed, any browser will mandate that this immediate certificate be present.
Types of SSL Certificates
There are three main types of SSL certificates available at the present time, an extended validation (EV SSL), an organization validation (OV SSL), and the domain validated (DV SSL). The security and encryption levels for each of these three types are the same, but what’s different among them is the verification process and the vetting which is used, as well as the look and feel of the browser bar.
The EV SSL certificate is issued after the certificate authority validates all of the following information:
- The identity of the applying organization is in sync with official records.
- The applying entity has the exclusive right to use the specified domain name in the certificate.
- The legal, physical, and functional existence of the applying party is valid.
- The applying party has properly authorized the issuance of an EV SSL certificate.
Organization Validated certificates (OV SSL) is somewhat less stringent than the Extended Validation certificates offered, since the Certificate Authority only checks the applicant’s right to use a certain domain name, plus some limited vetting of the organization.
The Domain Validated certificates (DV SSL) calls for the Certificate Authority to check the applicant’s right to use a certain domain name, but no actual company data is vetted. This means that all information is still encrypted, but you can’t be absolutely certain of who’s at the receiving end of any transmission.
The DV SSL certificates are most often used by businesses which are in need of a low-cost SSL, and which don’t want to go through the hassle of submitting documentation to verify their identity.
HostUpon SSL Certificates
Most of the hosting company offers various types of SSL certificates for customers. At HostUpon, you will get 2 different types of SSL certificates
- Premium SSL certificate – This certificate will cover any single domain name and it’s ‘www’ variation. Your website will turn to HTTPS with a green padlock in web browsers.
- Premium WildCard SSL certificate – This certificate will cover your domain and all the sub-domains. This is ideal if your website have multiple sub-domains that need to have HTTPS.
Here’s how you can purchase an SSL certificate from HostUpon.





Add comment